publications
ordered by date
2024
-
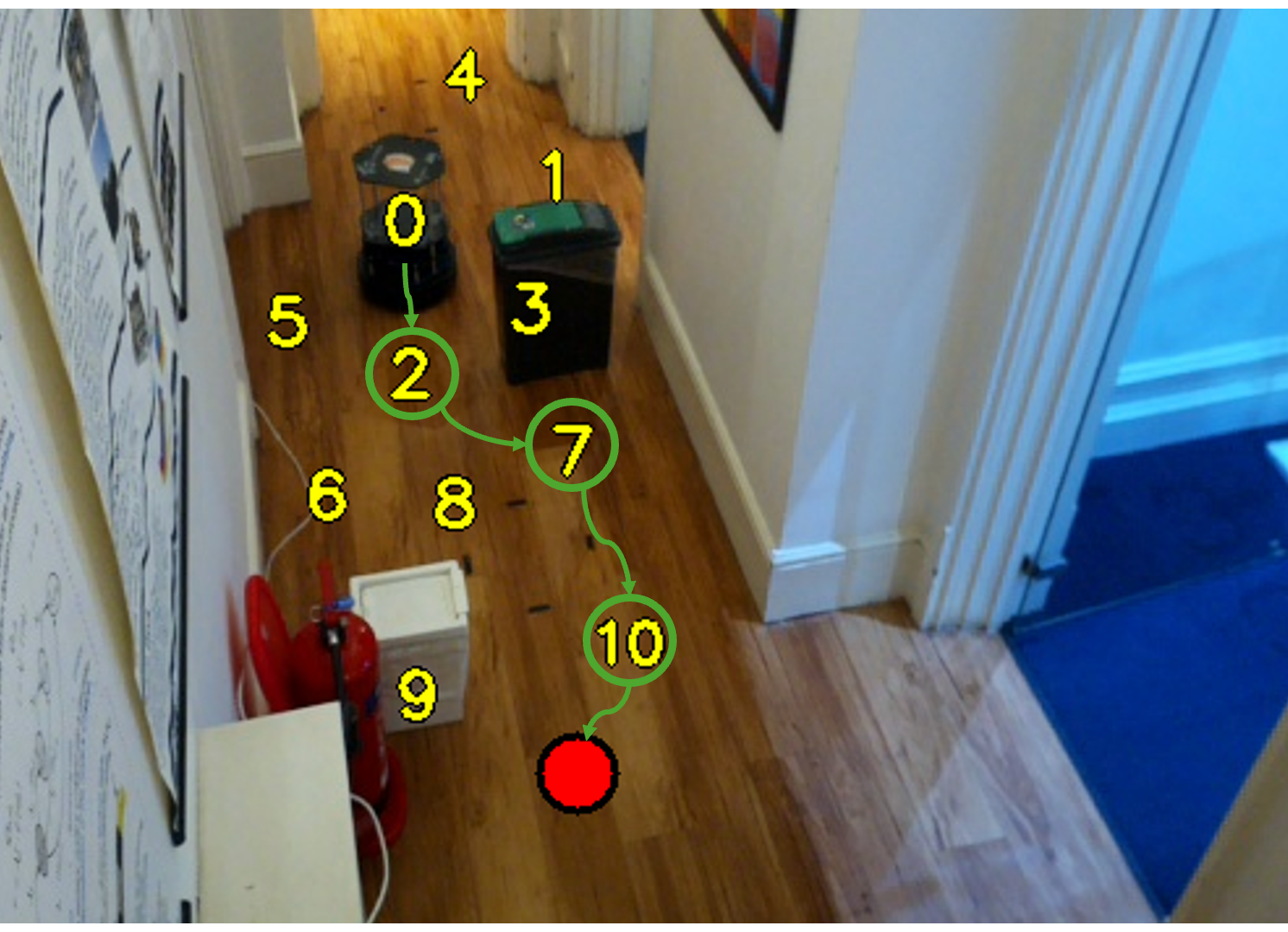 Select2Plan: Training-Free ICL-Based Planning through VQA and Memory RetrievalBuoso Davide , Robinson Luke , Averta Giuseppe , and 3 more authors2024
Select2Plan: Training-Free ICL-Based Planning through VQA and Memory RetrievalBuoso Davide , Robinson Luke , Averta Giuseppe , and 3 more authors2024This study explores the potential of off-the-shelf Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for high-level robot planning in the context of autonomous navigation. Indeed, while most of existing learning-based approaches for path planning require extensive task-specific training/fine-tuning, we demonstrate how such training can be avoided for most practical cases. To do this, we introduce Select2Plan (S2P), a novel training-free frame work for high-level robot planning which completely eliminates the need for fine-tuning or specialised training. By leveraging structured Visual Question-Answering (VQA) and In-Context Learning (ICL), our approach drastically reduces the need for data collection, requiring a fraction of the task-specific data typically used by trained models, or even relying only on online data. Our method facilitates the effective use of a generally trained VLM in a flexible and cost-efficient way, and does not require additional sensing except for a simple monocular camera. We demonstrate its adaptability across various scene types, context sources, and sensing setups. We evaluate our approach in two distinct scenarios: traditional First-Person View (FPV) and infrastructure-driven Third-Person View (TPV) navigation, demonstrating the flexibility and simplicity of our method. Our technique significantly enhances the navigational capabilities of a baseline VLM of approximately 50% in TPV scenario, and is comparable to trained models in the FPV one, with as few as 20 demonstrations.
-
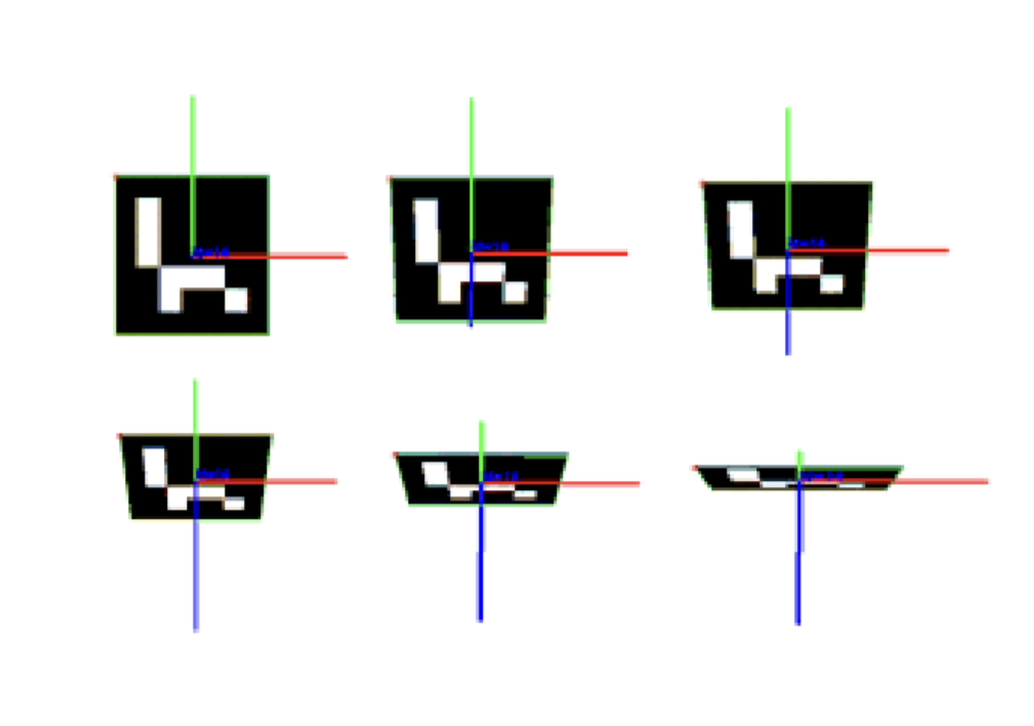 Enhanced Localization of ArUco Markers for Autonomous Robotics: A Comparative StudyMinervini Alessandro , Buoso Davide , Quito Casas Jean Carlos , and 4 more authors2024
Enhanced Localization of ArUco Markers for Autonomous Robotics: A Comparative StudyMinervini Alessandro , Buoso Davide , Quito Casas Jean Carlos , and 4 more authors2024Autonomous drone technology increasingly enables their use in diverse applications, offering cost and time benefits in precision agriculture and surveillance. They are especially efficient in search and rescue and exploring hard-to-access areas. Navigating indoor settings and partially known environments poses significant challenges in autonomous robotics. This paper introduces a novel method that leverages depth image data to substantially improve performance in these contexts. We elucidate the method’s design, showcasing its dependability and advantages over conventional approaches. Furthermore, the paper delineates the critical procedures for effective autonomous robot guidance, tackling complex obstacles inherent to the field.
-
 SpanLuke: Enhancing Legal NER using SpanMarker and LoRA (NP)Buoso Davide , Capuano Enrico , Caselli Andrea , and 1 more author2024
SpanLuke: Enhancing Legal NER using SpanMarker and LoRA (NP)Buoso Davide , Capuano Enrico , Caselli Andrea , and 1 more author2024Legal Named Entity Recognition is a focal point in NLP systems in legal domain, due to its potential to streamline processes and enhance decision-making accuracy. This paper delves into the SpanMarker technique for span-level representation of entity, the LUKE model for enhanced entity recognition and LoRA for efficient fine-tuning of large models. The study evaluates these methodologies, individually and in synergy, to improve the accuracy and performance of legal NLP systems. Additionally, a new dataset (EDGAR-NER) has been explored. In-depth experimentation reveals the potential of these approaches. This research contributes to ongoing efforts in leveraging NLP to enhance legal text process, reducing the time needed to train models to achieve this goal.
2023
-
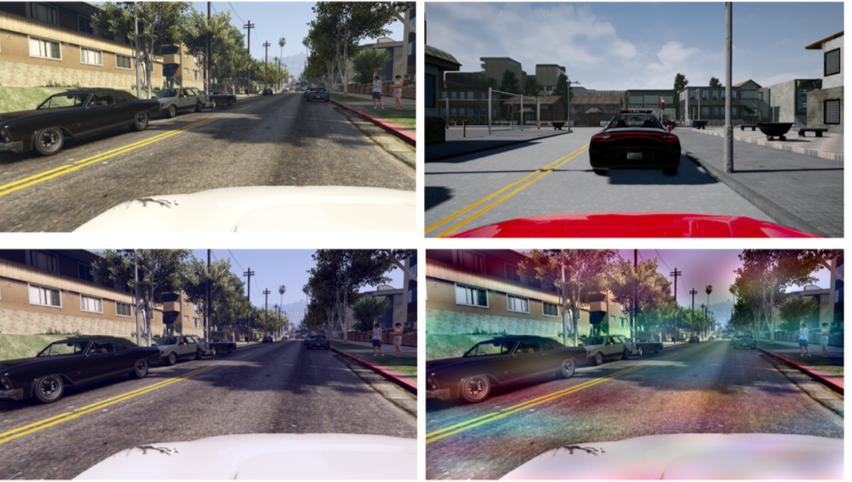 Exploring Federated Learning for Semantic Segmentation in Autonomous Driving and Satellite Images Scenarios (NP)Buoso Davide , Castiglia Marco , and Zuliani Giacomo2023
Exploring Federated Learning for Semantic Segmentation in Autonomous Driving and Satellite Images Scenarios (NP)Buoso Davide , Castiglia Marco , and Zuliani Giacomo2023This project explores the application of Federated Learning (FL) to the task of Semantic Segmentation (SS), with a focus on preserving client privacy while utilizing their data for model training. The proposed approach involves a centralized server pre-training phase on a labeled dataset, incorporating a style-transfer technique for domain adaptation. In the federated decentralized setting, our approach tackles the challenge of absent labels on client data. By leveraging pseudo-labels and self-training, the approach enables the utilization of unlabeled client images, effectively addressing the issue of limited ground truth availability. The report also provides additional insights into extending the applicability of this approach to domains beyond self-driving cars, such as satellite imagery. Additionally, an intriguing possibility explored in this project is the integration of a transformer model into the existing framework, presenting a promising alternative to the commonly employed CNN architectures.